Difference between revisions of "Chapter 26 Problem 40"
(Created page with "==Problem== thumb|right|Resistance is futile! Twelve resistors, each of resistance R, are connected as the edges of a cube. Determine the equi...") |
(→(a)) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
Insert a probe battery between points (a) and (b). Let's label the current drawn from this probe battery as I | Insert a probe battery between points (a) and (b). Let's label the current drawn from this probe battery as I | ||
| − | This setup has a symmetry plane between abed, so the current split at junction a will be | + | This setup has a symmetry plane between abed, so the current split at junction a will be |
| + | |||
<math>I=I_1+I_1+I_2</math> | <math>I=I_1+I_1+I_2</math> | ||
| − | Another symmetry is that the afhe plane is the mirror cdgb (since one has the current I entering, and the other has the current leaving) thus we have the same currents in erverse directions in those planes. | + | Another symmetry is that the afhe plane is the mirror cdgb (since one has the current I entering, and the other has the current leaving) thus we have the same currents in erverse directions in those planes. |
| + | *<math>I=2I_1+I_2</math> | ||
| + | *<math>I_3+I_4=I_1</math> | ||
| + | *<math>I_5=2I_4</math> | ||
| + | *<math>0=-2 I_1 R -I_3 R + I_2 R</math> | ||
| + | *<math>0=-2 I_4 R -I_5 R + I_3 R</math> | ||
| + | *<math>0=\mathcal{E}-2 I_2 R </math> | ||
===(b)=== | ===(b)=== | ||
Revision as of 20:02, 30 March 2019
Problem
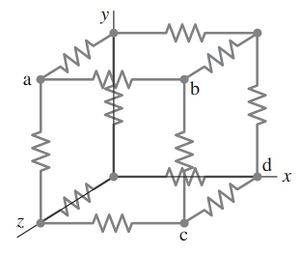
Twelve resistors, each of resistance R, are connected as the edges of a cube. Determine the equivalent resistance
(a) between points a and b, the ends of a side;
(b) between points a and c, the ends of a face diagonal;
(c) between points a and d, the ends of the volume diagonal.
[Hint: Apply an emf and determine currents; use symmetry at junctions.]
solution
(a)
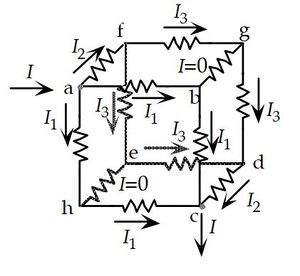
Insert a probe battery between points (a) and (b). Let's label the current drawn from this probe battery as I
This setup has a symmetry plane between abed, so the current split at junction a will be
Another symmetry is that the afhe plane is the mirror cdgb (since one has the current I entering, and the other has the current leaving) thus we have the same currents in erverse directions in those planes.
(b)
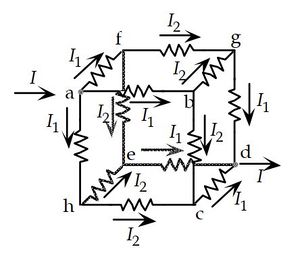
Insert a probe battery between points (a) and (c). Let's label the current drawn from this probe battery as I
(c)
Insert a probe battery between points (a) and (d). Let's label the current drawn from this probe battery as I