Difference between revisions of "Chapter 29 Problem 35"
From 105/106 Lecture Notes by OBM
(Created page with "==Problem== 300px|center|Wires and currents A short section of wire, of length <math>a</math>, is moving with velocity <math>\vec{v}</math> ,...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Problem== | ==Problem== | ||
[[File:Chapter29Problem35q.png|300px|center|Wires and currents]] | [[File:Chapter29Problem35q.png|300px|center|Wires and currents]] | ||
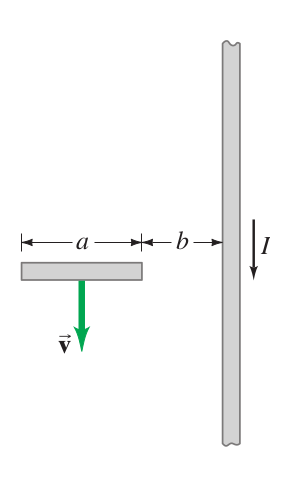
| − | A short section of wire, of length <math>a</math>, is moving with velocity <math>\vec{v}</math> , parallel to a very long wire carrying a current <math>I</math>. The near end of the wire section is a distance <math>b</math> from the long wire. Assuming the vertical wire is very long compared to <math>a + b</math>, determine the emf between the ends of the short section. Assume <math>\vec{v}<math> is | + | A short section of wire, of length <math>a</math>, is moving with velocity <math>\vec{v}</math> , parallel to a very long wire carrying a current <math>I</math>. The near end of the wire section is a distance <math>b</math> from the long wire. Assuming the vertical wire is very long compared to <math>a + b</math>, determine the emf between the ends of the short section. Assume <math>\vec{v}</math> is |
(a) in the same direction as <math>I</math>, | (a) in the same direction as <math>I</math>, | ||
(b) in the opposite direction to <math>I</math>. | (b) in the opposite direction to <math>I</math>. | ||
Revision as of 07:21, 30 April 2019
Problem
A short section of wire, of length , is moving with velocity , parallel to a very long wire carrying a current . The near end of the wire section is a distance from the long wire. Assuming the vertical wire is very long compared to , determine the emf between the ends of the short section. Assume is
(a) in the same direction as ,
(b) in the opposite direction to .