|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | __NOTOC__ | | __NOTOC__ |
| − | == Problem == | + | == Problem == |
| | + | [[File:Chapter21Problem20q.png|130px|right|Free body diagram]] |
| | + | Two small charged spheres hang from cords of equal length <math>l</math> and make small angles <math>\theta_1</math> and <math>\theta_2</math> with the vertical. |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:Chapter21-Problem20-v1.png|400px|right|Free body diagram]] | + | (a) If <math>Q_1=Q</math>, <math>Q_2=2Q</math> and <math>m_1=m_2=m</math> |
| | + | determine the ratio <math>\theta_1 / \theta_2</math> |
| | + | |
| | + | (b) If <math>Q_1=Q</math>, <math>Q_2=2Q</math> and <math>m_1=m</math> <math>m_2=2m</math> |
| | + | determine the ratio <math>\theta_1 / \theta_2</math> |
| | + | |
| | + | (c) Estimate the distance between the spheres for each case. |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | == Solution == |
| | + | |
| | + | [[File:Chapter21-Problem20-v1.png|400px|center|Free body diagram]] |
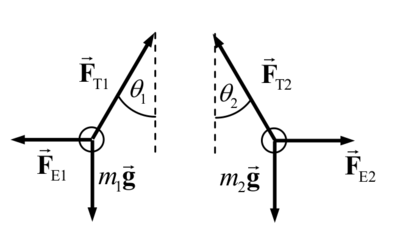
| | In the small angle approximation: | | In the small angle approximation: |
| | *the spheres only have horizontal displacement, and so the electric force of repulsion is always horizontal. | | *the spheres only have horizontal displacement, and so the electric force of repulsion is always horizontal. |
| Line 48: |
Line 62: |
| | | | |
| | <math>d=\left( \frac{3lkQ^2}{mg}\right)</math> | | <math>d=\left( \frac{3lkQ^2}{mg}\right)</math> |
| | + | |
| | + | <math></math> |
| | + | <math></math> |
| | + | <math></math> |
| | + | <math></math> |
| | + | <math></math> |
Revision as of 22:07, 16 February 2020
Problem
Two small charged spheres hang from cords of equal length  and make small angles
and make small angles  and
and  with the vertical.
with the vertical.
(a) If  ,
,  and
and  determine the ratio
determine the ratio 
(b) If  ,
,  and
and 
 determine the ratio
determine the ratio 
(c) Estimate the distance between the spheres for each case.
Solution
In the small angle approximation:
- the spheres only have horizontal displacement, and so the electric force of repulsion is always horizontal.

Since the spheres are in equilibrium, the net force in each direction is zero.
(a)


similarly

Apply Newton's third law:

Thus the answer is 1
(b)

(c)
The distance between the two spheres in small angle approximation is

in the first case  thus:
thus:



in the second case  thus:
thus: