Chapter 22 Problem 9
Problem
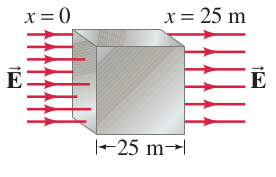
In a certain region of space, the electric field is constant in direction (say horizontal, in the direction), but its magnitude decreases from at to at . Determine the charge within a cubical box of side , where the box is oriented so that four of its sides are parallel to the field lines
Solution
Out of 6 faces the cube has, only the left and the right face contributes, since the electric field, , is perpendicular to the surface normal, ( for these 4 surfaces)
The surface normal on the left hand side is towards left (), and on the right hand side is right ()
Total flux is
The Gauss's law states the total flux through the surfaces of an enclosed volume is proportional to the charge it encapsulates
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_E=\E_\textrm{right}l^2-E_\textrm{left}l^2=\frac{Q_\textrm{encl}}{\epsilon_0}}
so the enclosed charge should be
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Q_\textrm{encl}=\left(\E_\textrm{right}-E_\textrm{left}\right)l^2\epsilon_0=\left(410 \textrm{N}/\textrm{C} - 560 \textrm{N}/\textrm{C}\right)\left(25 \textrm{m}\right)^2\left( 8.85\times 10^{-12} \textrm{C}^2/ \textrm{N} \textrm{m}^2\right) = -8.3 \times 10^{-7} \textrm{C}}