Chapter 23 Problem 83
Problem
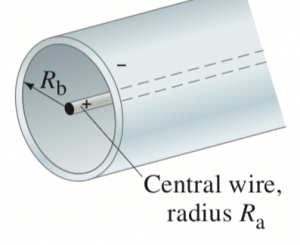
A Geiger counter is used to detect charged particles emitted by radioactive nuclei. It consists of a thin, positively charged central wire of radius surrounded by a concentric conducting cylinder of radius with an equal negative charge. The charge per unit length on the inner wire is (units ). The interior space between wire and cylinder is filled with low-pressure inert gas. Charged particles ionize some of these gas atoms; the resulting free electrons are attracted toward the positive central wire. If the radial electric field is strong enough, the freed electrons gain enough energy to ionize other atoms, causing an “avalanche” of electrons to strike the central wire, generating an electric “signal.” Find the expression for the electric field between the wire and the cylinder, and show that the potential difference between and is
Solution
This is a very straightforward application of the relationship between Electric field and potential. From the previous section, the electric field due to a line charge is radially outward with the magnitude
then







![{\displaystyle ={\frac {\lambda }{2\pi \epsilon _{0}}}\left[\ln R_{a}-\ln R_{b}\right]={\frac {\lambda }{2\pi \epsilon _{0}}}\ln \left({\frac {R_{b}}{R_{a}}}\right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2e0c68d674c055d4f449ec7e4f002cefb6ee6cd8)